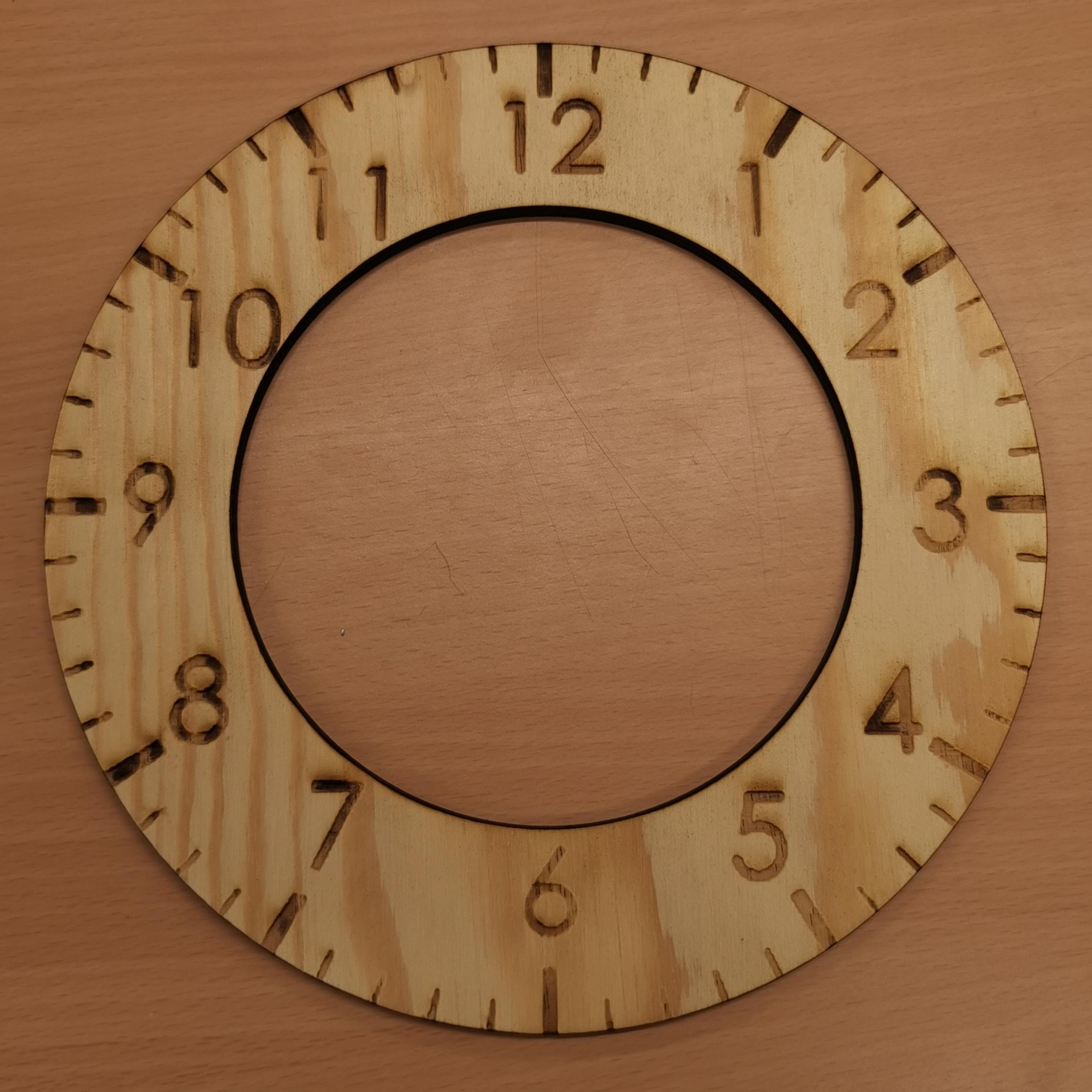
Laser Cutting and Engraving
Instruction Manual Lasercutter trotec speedy 100 C 40
Laser cutting and engraving is a precise manufacturing process that uses a focused laser beam to either cut through or engrave materials. The design begins in vector graphic software such as Adobe Illustrator, Inkscape, or CAD programs, where the artwork or part layout is created. This design is then converted into specific code, often G-code or a similar machine language, through control software like LightBurn or LaserGRBL, which directs the laser's movement, speed, power, and pattern during the process.
The most common type of laser used in this process is a CO2 laser, which efficiently cuts and engraves a variety of materials, including wood, acrylic, leather, fabric, some plastics, and even thin metals. The effectiveness largely depends on the laser power: higher power enables cutting thicker or denser materials, while lower power is suitable for delicate engraving. Adjusting parameters like speed and power ensures precision and prevents burning or melting.

In operation, the laser beam is guided by mirrors or galvo scanners to the material surface, where it heats and vaporizes the material along the programmed path. For cutting, the laser fully penetrates the material, separating parts. For engraving, it removes only a thin surface layer. The process is non-contact, meaning minimal mechanical stress on the material, which preserves its integrity and prevents deformation.
Advantages of laser cutting and engraving include high precision, repeatability, and versatility in handling complex shapes and fine details. However, it requires proper ventilation and safety measures because the laser emits potentially harmful fumes and intense light. Risks involve eye and skin damage if proper shielding and protective equipment are not used. Despite some operational costs, laser cutting offers a clean, efficient, and flexible method for manufacturing and creative applications.
